Describe the Organization of the Body Cavities
Line the thoracic cavity and cover the lungs. Abdominopelvic cavitythe abdominal cavity and the pelvic cavity in combination.
Cover organs win the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavity.
. A coelom is a special type of body cavity derived from the mesoderm or middle layer of germ cells present in an embryo. Contains the end of. Describe the organization of organismal complexity ie.
All matter in the universe is made of atoms which are made of sub-atomic particles like neutrons protons and electrons. A region in the thoracic cavity called the mediastinum separates the lungs. Contains ovaries ureters and bladder Abdominopelvic Cavity.
Levels of Organization in the Human Body. Line the walls of the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavity. Tissue is composed of groups of cells that possess a common function.
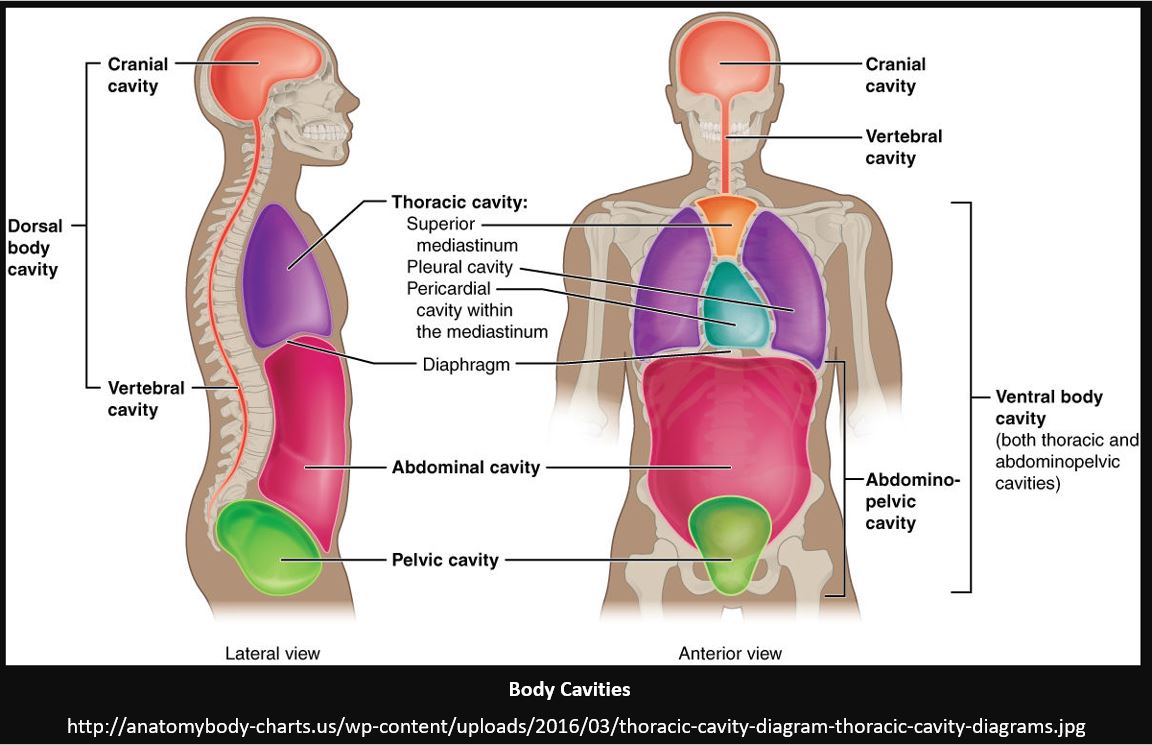
The cranial cavity contains the brain and other organs such as the pituitary gland an endocrine gland located below the brain. The cranial cavity 1 is located in the head and surrounded by the skull CRANIO means skull. The cranial cavity the cavity inside the skull or the cranium contains the brain.
The Organization and Structure of the Human Body The Organization and Structure of the Human Body The human body is made up of a complex structure of systems that all work together. The pleural cavities flank the pericardial cavity. Some organisms like sponges have no body cavities.
Acoelomate pseudocoelomate and eucoelomate. Tap card to see definition. Click card to see definition.
The human body like that of many other multicellular organisms is divided into a number of body cavities. A larger cavity called the ventral cavity and a smaller cavity called the dorsal cavity. Organisms with three distinct germ layers which form a body cavity are known as coelomates.
Contains the terminal portion of large intestine urinary bladder and internal reproductive organs. Molecules form organelles the basic component of cells. A body cavity is a fluid-filled space inside the body that holds and protects internal organs.
Include the stomach liver spleen gallbladder kidneys most of the intestines. Two Major Body Cavities. Up to 24 cash back PART III.
The Organization of the Human Body. Start studying Organization of the body organs and body cavities. Describe the organization of organismal complexity ie.
There are three serous membranes each with two layers. Atoms particles of matter combine to form molecules such as water. A visceral layer that adheres to the surface of the organ and a parietal layer that lines the body cavity.
Oral cavity nasal cavity orbital c middle ear cavities. In this interactive object learners examine the locations of major body cavities and their protective membranes. Thoracic cavitythe space occupied by the ventral internal organs superior to the diaphragm.
Each cavity contains organs that are organized no pun intended in a neat and orderly fashion. A drag-and-drop exercise completes the activity. Contains the heart and lungs Abdominal Cavity.
Human body cavities are separated by membranes and other structures. An imaginary line running across the hipbones and dividing the body into the abdominal and pelvic cavities. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
Be able to give examples of each gro. Divided into three parts. The body contains two major cavities.
Contains the stomach liver gallbladder pancreas spleen small intestines and most of the large intestine Pelvic cavity. 11 Describe the levels of structural organization that make up the human body. This region also contains the esophagus trachea thymus blood vessels and.
Ventral body cavitythe thoracic cavity the abdominal cavity and the pelvic cavity in combination. The pelvic cavity contains the. Surround the heart and cover its surface.
There are two principle body regions and these are broken up into smaller cavities. Right and left pleural cavities. The abdominal cavity contains the stomach intestines liver spleen gallbladder pancreas ureters and kidneys.
The body cavities are covered with a serous membrane that supports and protects the organs it encloses. Contains the gallbladder liver pancreas and stomach Pelvic Cavity. If you think back to the video I made over the directional terms youll know that ventral or anterior means toward the front of the body and dorsal or posterior means toward the back of the body.
The mediastinum region contains the pericardial cavity which holds the heart. Explain the three different types of body cavities found in bilateral animals ie. The thoracic cavity 2 also known as the chest cavity THORACO means chest is surrounded by the breastbone and ribs.
There are several levels of organization to this structure with each level more complex than the last. Body cavities are spaces within the body that surround internal organs. The two largest human body cavities are the ventral cavity and the dorsal cavity.
Contains the abdomen and pelvis. There are two principle body regions and these are broken up into smaller cavities. The spinal cavity is continuous with the cranial cavity.
The potential space cavity formed between the two layers is filled with a thin film of serous fluid. Others like segmented worms have many body cavities one present in each segment. Smaller cavities in the head.
The thoracic cavity is subdivided into smaller cavities. Houses the skull brain and spinal cavity Ventral Cavity. The right pleural cavity contains the right lung and the left pleural cavity contains the left lung.
The five body cavities include the following. Axial portion Appendicular portion Cranial cavity. The serous membrane has two layers one nested to the organ called the visceral layer and the outer one called the parietal layer Figure 14.
Body Cavities And Membranes Scientist Cindy

No comments for "Describe the Organization of the Body Cavities"
Post a Comment